Table of Contents
What Are Scud Clouds? A Guide to This Mysterious Weather Phenomenon
What are scud clouds? This is a question that has puzzled meteorologists for years. These mysterious clouds have been observed in many parts of the world, but their exact nature remains unknown. In this article, we will explore what scud clouds are, and offer some tips on how to identify them.
What’s a Scud cloud?
A Scud cloud is a low-hanging cloud that can form when moist air flows over colder air near the ground. Scud clouds look like ragged pieces of cotton candy and can be mistaken for tornadoes, especially when they’re accompanied by heavy rain and strong winds.
Scud clouds are usually found in front of thunderstorms, but they can also form ahead of cold fronts and warm fronts. They typically move faster than the main storm system, which is why they’re often seen as “outrunners.”
While Scud clouds don’t always produce severe weather, they can be a sign that dangerous conditions are on the way. If you see a Scud cloud, it’s important to stay aware of your surroundings and be prepared to take shelter if necessary.
Scud clouds got their name from the German word “scutum,” which means shield. They’re sometimes called “fragmentation clouds” because they can look like pieces of debris floating in the sky.
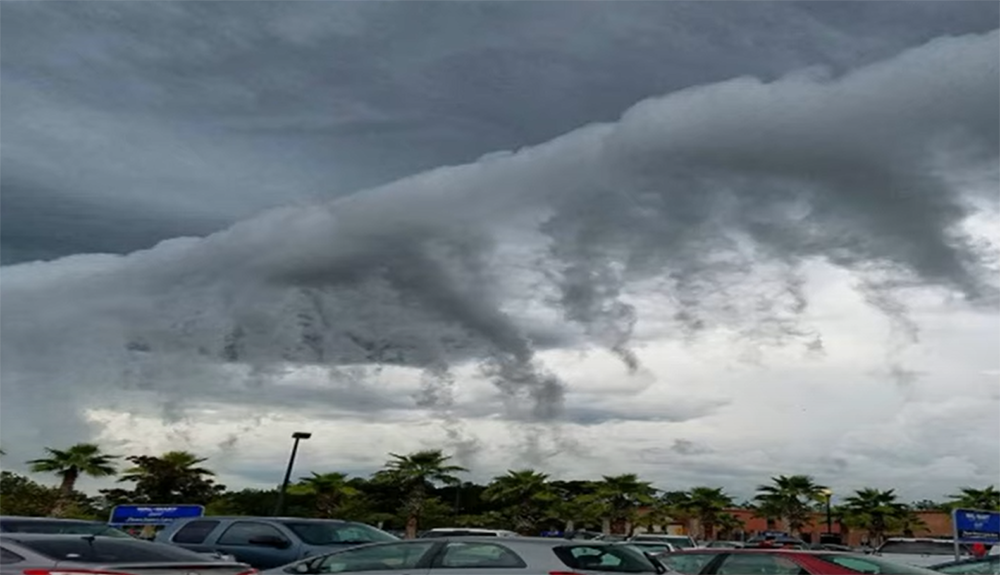

Scud clouds are usually found at altitudes between 2000 and 3000 feet, but they can form as low as 500 feet above the ground. [1]
While Scud clouds are often associated with severe weather, they can also form under stable conditions.
Formation of Scud Clouds
Scud clouds form when air near the ground is forced to rise quickly through a layer of stable air. This can happen when warm air rises over cold air, or when cold air moves under a layer of warmer air. Scud clouds are usually low-lying (less than 2000 feet above the ground) and have ragged, horizontal edges.
Scud clouds can be either cumuliform or stratiform in nature. Cumuliform scud clouds are the more common type, and have a lumpy or bumpy appearance. Stratiform scud clouds are flatter and smoother, with a uniform base.
What Weather Conditions are Associated with Scud Clouds?
Scud clouds often accompany thunderstorms, but can also be found in front of cold fronts and around areas of low pressure. While scud clouds can occur in any season, they are most common in spring and summer. This is because scud clouds need instability in the atmosphere to form, and this is more likely to happen when the air is warm.
When a cold front moves through an area, the leading edge of the colder air can cause scud cloud formation. These clouds will dissipate after the front has passed through. However, if there is enough moisture and instability in the atmosphere, they may persist and even grow into thunderstorms.
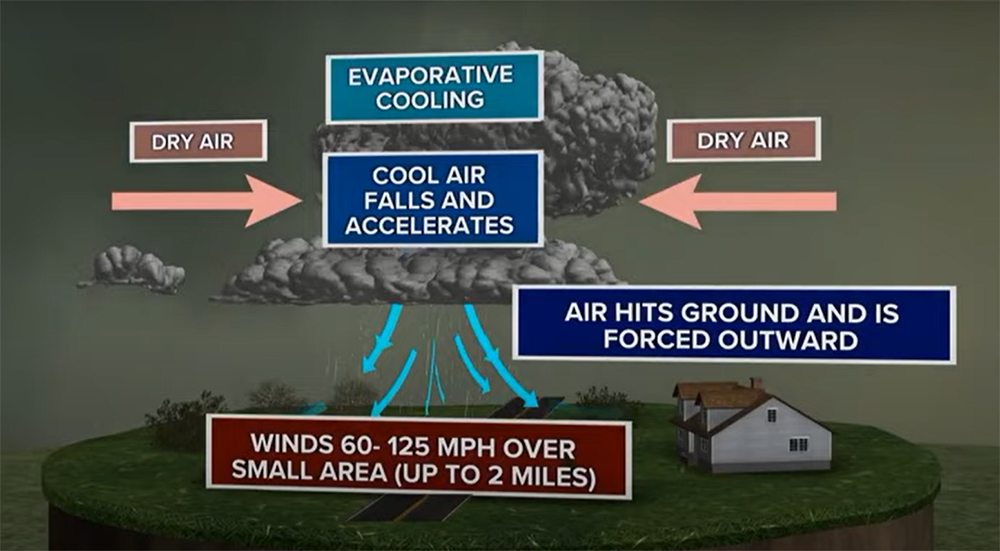
Areas of low pressure are another common location for scud clouds. These areas are usually associated with thunderstorms, but the scud clouds themselves are not necessarily convective. In fact, they can often be found in the stratiform region of a thunderstorm (the area where most of the rainfall is occurring).
Scud clouds can also form around mountains or other obstacles that force air to rise quickly. When this happens, the rising air cools and condenses, forming a cloud. This type of scud cloud is called an orographic cloud. [2]
Scud clouds are a fascinating weather phenomenon. While they are often associated with bad weather, they can also be beautiful and awe-inspiring. So next time you see a scud cloud, take a moment to appreciate its unique form.
The Difference Between Scud clouds And Wall Clouds
Have you ever seen a scud cloud? Scud clouds are low-hanging, ragged clouds that are often associated with thunderstorms. They can be hard to spot because they blend in with the storm clouds above them.
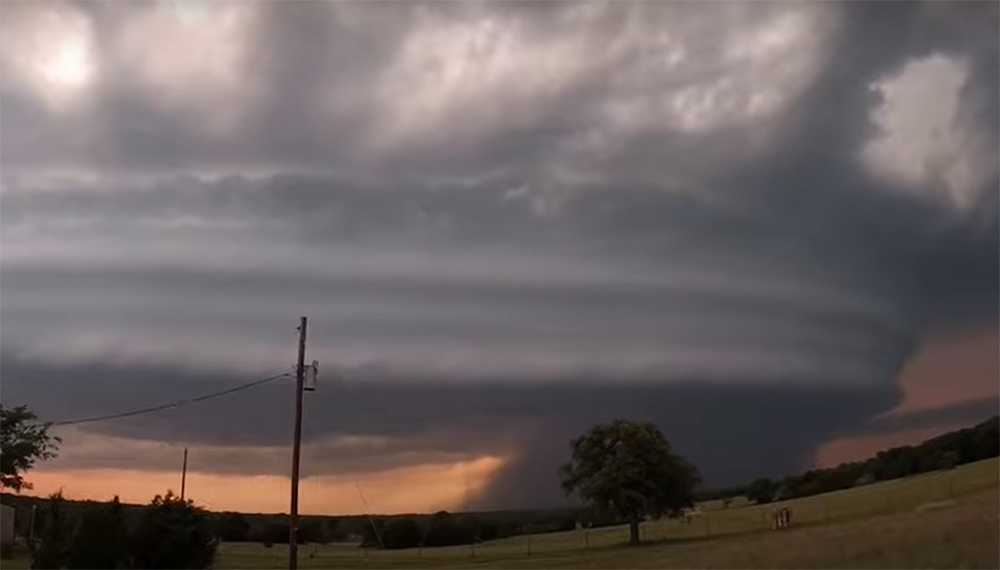

What sets scud clouds apart from other types of clouds is their shape and size. Scud clouds are smaller than cumulus or stratus clouds, and they have a more irregular shape. They often look like pieces of cotton or wool that have been blown around by the wind.
Scud clouds are also different from wall clouds in one important way: they are not connected to the base of the thunderstorm. Wall clouds extend down from the base of the thunderstorm.
Scud clouds often form when warm air rises from the ground and hits a layer of cooler air. This can happen during thunderstorms, but it can also happen in other situations, like when a cold front moves through an area.
Scud clouds usually don’t last very long, and they often dissipate before a thunderstorm arrives. However, they can sometimes be one of the first signs that a thunderstorm is on its way. If you see scud clouds forming, it’s a good idea to keep an eye on the sky and be prepared to take shelter if necessary.
Wall clouds, on the other hand, are a sign that a thunderstorm is already happening. If you see a wall cloud, it means that you should take shelter immediately. [3]
Scud clouds are relatively rare, but they can be found all over the world. They’re most common in areas with warm weather, like the tropics. However, they can also form in temperate and even cold climates.
The Difference Between A Scud Cloud And Funnel Clouds
When a scud cloud forms, it is often mistaken for a funnel cloud. However, there are some key differences between the two. Scud clouds don’t have a rotating base like funnel clouds do. Instead, it is simply a low-hanging cloud that can sometimes form in the shape of a tube. Additionally, scud clouds are usually much smaller than funnel clouds and do not extend all the way to the ground. Lastly, scud clouds form during thunderstorms while funnel clouds generally occur before or after storms.
Despite these differences, scud clouds can still be dangerous. If you see one forming, it’s important to stay away from any nearby bodies of water as they can quickly turn into tornadoes. [4]
The Difference Between Scud And Tornado Clouds

Scud clouds are also generally smaller and lower to the ground than tornado clouds. They can be as low as 20 feet (six meters) above the ground, while tornado clouds can extend up to 60,000 feet (18 kilometers) into the sky. Scud cloud formations are also not as organized as tornado cloud formations. Tornadoes typically have a cyclonic rotation, while scuds do not.
For one, scud clouds typically form in areas of low pressure, while tornadoes form in areas of high pressure. Additionally, scud clouds are usually not as dense or as dark as tornado clouds. Finally, scud clouds typically move more slowly than tornadoes.
The Difference Between Scud Clouds And Gustnadoes
When a thunderstorm’s outflow boundary – the leading edge of the storm’s cooler, drier air – encounters warm, humid air ahead of it, that can set off a rapid spin in the lower atmosphere. The result is what’s called a gustnado: a tornado-like rotating column of air that extends from the base of the thunderstorm down to the ground. Gustnadoes are usually weak and short-lived, but they can occasionally be strong enough to damage property or injure people.
When humid air rises very rapidly and adiabatically cools, it creates scud clouds. (that is, without exchanging heat with its surroundings). As the air rises and expands, it cools and condenses into water droplets, forming the cloud. Scud clouds are seen behind thunderstorms, where they’re being pushed along by the storm’s outflow boundary.
While scud clouds and gustnadoes can both be spawned by thunderstorms, they’re quite different phenomena. Gustnadoes form when a rotating column of air is spun up by the meeting of two different air masses. Scud clouds, on the other hand, form when moist air rises quickly and cools adiabatically. Because they have different causes, scud clouds and gustnadoes also tend to have different appearances. Scud clouds are usually wispy and diffuse, while gustnadoes tend to be more compact and well-defined.
The Difference Between Scud Clouds And Shelf Clouds
Most people have probably seen a shelf cloud and thought it was a thunderstorm about to roll in. And while scud clouds can be associated with storms, they differ from shelf clouds in a few key ways.
For starters, scud clouds are usually lower to the ground than shelf clouds. They also tend to be less organized and more ragged in appearance. Finally, scud clouds don’t typically form along the leading edge of a thunderstorm like shelf clouds do.

Shelf clouds are usually a sign that bad weather is on the way, but scud clouds form in both stable and unstable air. So if you see a scud cloud, it doesn’t necessarily mean that a storm is brewing.
Scud clouds may also be produced along the leading edge of a cold front when warm air is rapidly replaced by chilly air. This can cause turbulence and strong winds, so it’s always important to be aware of your surroundings if you see scud clouds starting to form.
FAQ
What causes a scud cloud?
A scud cloud is caused by moist air being forced upwards, usually by a cold front or thunderstorm. The air cools as it rises and the water vapor condenses into clouds.
Scud clouds can also form when warm air moves over a cold surface, such as a snow-covered field. The warm air cools as it comes into contact with the colder ground, causing the water vapor to condense and form clouds.
In some cases, scud clouds can be mistaken for tornadoes. However, there are several key differences between these two weather phenomena.
If you see a scud cloud, it’s important to stay aware of your surroundings and monitor the weather conditions. Scud clouds can quickly turn into severe thunderstorms or tornadoes, so it’s important to be prepared for rapidly changing weather conditions.
What is a scud bomb cloud?
A scud bomb cloud is a type of cumulonimbus cloud, which is a thunderstorm cloud. It gets its name from the fact that it looks like a puff of smoke or mist rising from the ground. These clouds are usually found in tropical areas and can grow to be very large, reaching heights of up to 15 kilometers! Scud clouds are often associated with severe weather events such as tornadoes, hailstorms, and flash flooding.
While they may look harmless, scud clouds can actually be quite dangerous. If you find yourself caught in one of these storms, it’s important to seek shelter immediately and stay away from any bodies of water. If you’re caught outdoors, try to find a low-lying area such as a ditch or culvert to take shelter in. [5]
What does scud mean in weather?
The term “scud” is used to describe low-hanging clouds that are often associated with thunderstorms. These clouds can be very dangerous because they can produce strong winds and hail. Scud clouds are also known as cumulonimbus incus clouds.
Scud clouds are most frequent in the spring and summer months, but they can appear any time of year. They usually form when warm air rises quickly and cools off at a higher altitude. This cooling process creates instability in the atmosphere, which can lead to severe weather conditions.
Scud clouds are often mistaken for cirrus clouds, but there are some key differences between the two. Cirrus clouds are generally much higher up in the sky and they are not typically associated with severe weather.
Is a scud cloud a funnel cloud?
No, a scud cloud is not a funnel cloud. Scud clouds are low-lying clouds that form along the front of a thunderstorm. They often look like ragged pieces of cumulus clouds that are being blown away from the storm. They can sometimes contain precipitation, but they are not capable of producing tornadoes.
Funnel clouds, on the other hand, are rotating columns of air that extend from the base of a thunderstorm all the way to the ground. If a funnel cloud reaches the ground, it becomes a tornado. Tornadoes can cause catastrophic damage and should always be taken seriously.
Are Scud Clouds Dangerous?
The answer to this question is a resounding yes! Scud clouds are extremely dangerous, and can pose a serious threat to both aircraft and ground vehicles. If you find yourself in an area where scud clouds are present, it is important to take cover immediately and wait for the storm to pass.
Scud clouds are often associated with thunderstorms, so it is important to be aware of your surroundings and monitor the weather conditions before venturing out into scud territory. If possible, try to avoid flying or driving through scud clouds, as they can cause visibility problems and make it difficult to navigate.
If you must travel through a scud cloud, be sure to use caution and allow extra time for your journey.
Do Scud Clouds Rotate?
The answer to this question is a little complicated. Scud clouds can rotate, but they don’t always rotate. Sometimes scud clouds will form around areas of low pressure, and these low-pressure systems can cause the cloud to rotate. However, not all scud clouds are associated with low-pressure systems. So, it really depends on the individual cloud formation.
Another factor that can influence a scud cloud’s rotation is the wind. If the wind is blowing from one direction, it can cause the cloud to rotate. This is because the air pressure around the cloud is not equal. The side of the cloud that is facing into the wind will have more pressure than the side that is facing away from the wind. This unequal pressure can cause the cloud to spin. [6]
So, in short, scud clouds can rotate, but it depends on a variety of factors. If you see a scud cloud rotating, it could be due to a low-pressure system or strong winds. But if you see a scud cloud that isn’t rotating, don’t worry – it’s perfectly normal!
Useful Video: Ask Ellen: What is a SCUD?
Conclusion
In conclusion, Scud clouds are a fascinating weather phenomenon that can be both beautiful and dangerous. Hopefully, this guide has given you a better understanding of what they are and how to spot them. Remember, if you see one forming near you, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and take shelter. Stay safe out there!
References:
- https://www.accuweather.com/en/weather-news/what-are-scud-clouds/198999
- https://timswww.com.au/scud-clouds-weather-creepy-clouds-that-form-under-thunderstorms/
- https://www.whsv.com/content/news/Scud-clouds-vs-Wall-clouds-whats-the-difference-569114741.html
- https://www.nwahomepage.com/weather/weather-101/weather-101-look-its-a-funnel-cloud-or-is-it-difference-between-funnel-clouds-and-scud-clouds/
- https://www.cbs58.com/news/scary-clouds-explainer
- https://www.indherald.com/2021/04/09/eye-to-the-sky-funnel-clouds-vs-scud-clouds-identifying-the-differences/





Leave a Reply